TWHL: WikiCode Syntax Last edited 2 years ago2022-09-25 02:27:37 UTC
TWHL uses a custom text syntax that we call WikiCode. It is a combination of Markdown and BBCode, with a few extra things to spice it up. If you're familiar with either of these markup systems, you shouldn't have too much trouble.
Here is TWHL's library of smilies and their corresponding text representations. Simply type the text and it will be replaced with a smiley image in the post.

















































The syntax can look something like this:
Where every field aside from
youtube.com/watch?v=oGlhgVz5r6E
Once you have the ID, you can use the
Quotes can be nested quite easily:
If the first line of your panel content starts with
Then you put that ID in a vault tag like this:
To create a table, you use one line of text per table row. For a header row, start the line with
This table can be created by typing this:
Phew! That's everything! I know there's a lot of stuff here, but don't worry too much about it. If you need to do a particular thing, just come back to this page later so you can refresh your memory.
Basic text formatting
There are two ways to do basic text formatting - the Markdown way and the BBCode way. Markdown style is usually faster to type, but BBCode is generally more flexible.| Format | Markdown style | BBCode style |
|---|---|---|
| Bold text | *Bold text* | [b]Bold text[/b] |
| Italic text | /Italic text/ | [i]Italic text[/i] |
| Underlined text | _Underlined text_ | [u]Underlined text[/u] |
| Strikethrough text | ~Strikethrough text~ | [s]Strikethrough text[/s] |
Inline code | `Inline code` | [ code ]Inline code[ /code ] (remove extra spaces) |
Smilies/emoticons/emoji
Before the land of smartphones and dedicated Unicode glyphs, emoji were known as 'smilies', and were not text, but images! Bizarre, I know. TWHL has complete Unicode support, so go nuts with your smartphone keyboards and you won't have any issues with favourites such asU+1F4A9: PILE OF POO: 💩. For us plebs using desktop browsers, though, you can also use the traditional smilies from the good ol' days.Here is TWHL's library of smilies and their corresponding text representations. Simply type the text and it will be replaced with a smiley image in the post.





































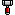












:aggrieved: :aghast: :x :badass: :confused: :cry: :cyclops: :lol: :| :furious:
:glad: :heart: :D :nervous: :nuke: :nuts: :quizzical: :roll: :( :)
:o :thebox: :thefinger: :tired: :P :cool: :\ :biggrin: ;) :zonked:
:sarcastic: :combine: :gak: :^_^: :pwned: :target: :ninja: :hammer: :pirate: :walter:
:plastered: :zomg: :heartbreak: :ciggie: :combines: :crowbar: :death: :freeman: :hecu: :nya:Linking
On the web, linking is one of the more useful things you can do. So, of course there are multiple ways you can link to things using WikiCode. To use auto-linking, make sure the URL starts withhttp://. Be careful, because some browsers don't include this by default.
| Link method | Markup | Result |
|---|---|---|
| Standard link | [url]http://example.com[/url] | http://example.com |
| Custom link | [url=http://example.com]Example link[/url] | Example link |
| Standard email link | [email]test@example.com[/email] | test@example.com |
| Custom email link | [email=test@example.com]Example email link[/email] | Example email link |
| Quick link | [http://example.com] | http://example.com |
| Custom quick link | [http://example.com|Example link] | Example link |
| Link to TWHL wiki page | [[Home]] | Home |
| Custom link to TWHL wiki page | [[Home|Example link]] | Example link |
| Auto-link | http://example.com | http://example.com |
Images
Embedding images is another useful thing to do, especially on a wiki. Because it's important, there's a few different ways that images can be added to a post. The output isn't shown in this case because images can take a fair amount of space, but you can experiment by using the preview button when typing a post.| Format | Markup | Notes |
|---|---|---|
| Normal image | [img]http://example.com/example.jpg[/img] | Embed a normal image (breaks text top and bottom) |
| Link image | [url=http://example.com][img]http://example.com/example.jpg[/img][/url] | Clickable to open a URL |
| Inline image | [simg]http://example.com/example.jpg[/simg] | Embed a small image (inline with text) |
| Advanced image | [img:http://example.com/example.jpg] | See details on the advanced image format below |
| Link to TWHL wiki image | [img:example.jpg] | example.jpg is the title of the wiki upload |
Pasting images
If you have an image on your clipboard (usually from taking a screenshot with thePrtSc key, snipping tool in Windows 7, or Win+Shift+S in Windows 10), you can press Ctrl+V into a TWHL textbox to upload the image and insert the required WikiCode to embed the image. This will not work if you have an image file on your clipboard - it must be an actual image.
Using the advanced image tag
Sometimes you wish you had more flexibility when embedding images. Well, now you do! The advanced image tag gives you a few options when adding images to your post.The syntax can look something like this:
[img:example.jpg|url:http://example.com|size_modifier|position_modifier|caption_text]Where every field aside from
img: is optional. An explanation of each option:
url:- should explain itself. Use this to make the image link to a website when you click on it.size_modifier- by default, the image tries to fill the width of the page. You can use the size modifier to change it to a fixed size. Valid values are:thumb,small,medium, andlarge.position_modifier- by default, the image is centered and text will be wrapped above and below the image. You can use the position modifier to change the position and make the text flow around the image. Valid values areinline,left,right, andcenter.caption_text- if you type anything aside from the values above, it will be treated as a caption to the image. You can only use plain text in the caption.
[img:] with [video:] or [audio:] to use them. You can embed external video and audio as well, but note that some formats are not supported on some browsers, so it might not work for everyone. The safest formats to use are mp3 for audio, and mp4 for video.
Youtube
Embedding Youtube videos was an often-requested feature in TWHL, and now everybody can do it. To embed the video, you first need to find the video ID. You can find this in the URL of any Youtube video - it's a string of 10 or so letters and numbers. It's underlined in the example below.youtube.com/watch?v=oGlhgVz5r6E
Once you have the ID, you can use the
[youtube] tag to add it to your post:
[youtube]oGlhgVz5r6E[/youtube][img:] tag, but you can't use the url:, inline, or thumb options in the tag. An example:
[youtube:oGlhgVz5r6E|left|medium|This is the caption text]Headings
Headings follow the HTML trend by having six levels. To use a heading, start a new line with= symbols. The more symbols you use, the smaller the heading will be.
These headings are generated by this code:
= Heading 1 (Largest)
== Heading 2
=== Heading 3
==== Heading 4
===== Heading 5
====== Heading 6 (Smallest)Lists
You can make lists by using* for bullet points or # for ordered lists. You can create sub-lists by adding extra symbols. You can mix list types on each level.
The markup for the above looks like:
* List item 1
* List item 2
** List item 2.1
** List item 2.2
# Step 1
# Step 2
#* Be sure to do step 1 before step 2!Quotes
Often you want to quote another user when you are replying to them. Again, there are two different ways to quote users.Markdown style quotesThe code looks like this:
This is the second line of the quote
> Markdown style quotes
> This is the second line of the quoteQuotes can be nested quite easily:
And the markup:This is the parent quoteThis is the child quote
>> This is the parent quote
> This is the child quote[quote] BBCode tag. These quotes can be nested as well. The new lines are not required, they are simply there to make it easier to read the example.
[quote]
[quote]This is the parent quote[/quote]
This is the child quote
[/quote]GLaDOS said:Oh, hi. So, how are you holding up? Because I'm a potato!Which can be done like this:
[quote=GLaDOS]Oh, hi. So, how are you holding up? Because I'm a potato![/quote]Panels
Panels are a simple way to separate some content into its own block. Panels can't be nested within each other, but they can contain any other markup you want. To create a panel, simply mark the start of the content with~~~. The end of the panel will be marked by the next line that starts with ~~~.If the first line of your panel content starts with
:, it will be used as the panel title.
Panels can have different colours as well. The options are: message (green), info (blue), warning (yellow), and error (red). To use these colours, put the option after the ~~~ at the beginning of the panel.
Horizontal line
This is a pretty simple one. Simply have a line of text that has nothing but---. It'll draw a line that's useful for separating sections of text in a post. It looks like this:
Wiki category
This is the only tag that's specific to the wiki. You can use it in other places, but it will just be ignored. Add this tag to categorise wiki pages. Make sure you spell the category correctly, or the page will link to the wrong category. Here's some examples:[cat:Put Category Name Here]
[cat:Source Tutorials]
[cat:Requires Further Detail]Embedded vault
If you're posting on a WIP thread or want to show off your new map or mod, you can embed the map vault item into the post. This is also good for posting example maps on a wiki page. To embed a vault item you need to know the ID of the item. You can find this at the end of the URL on the vault page. For example: twhl.info/vault/view/1234Then you put that ID in a vault tag like this:
[vault:1234]Tables
If you want to get really fancy with your post, you can insert a table. The contents of a table can only be inline - for example, inline images, text formatting, links, and so on. You can't put stuff like Youtube videos or quotes in a table.To create a table, you use one line of text per table row. For a header row, start the line with
|=. For a normal row, start the line with |-. After that, simply enter the contents of each column, separated by a | character. For example:
| Header 1 | Header 2 |
|---|---|
| Value 1 | Value 2 |
|= Header 1 | Header 2
|- Value 1 | Value 2Advanced text formatting
These advanced text formatting techniques are not possible using the Markdown style.| Format | BBCode | Notes |
|---|---|---|
| Colour text | [font=red]Colour text[/font] | Can use any colour name from the CSS colour list |
| Colour text 2 | [font=#FEA320]Colour text 2[/font] | Can use any RGB hex value |
| Large text | [font size=20]Large text[/font] | Can use sizes between 6px and 40px |
| Small text | [font size=8]Small text[/font] | The standard text size is 14px |
| Large red text | [font color=red size=20]Large text[/font] | Both size and colour can be combined. Remember to use the American spelling for "color". |
| Spoiler tag | [spoiler]Spoiler tag[/spoiler] | Don't spoil stuff for others! |
| There's a resonance cascade | [spoiler=Half-Life]There's a resonance cascade[/spoiler] | It's polite to specify what game/movie/etc. the spoiler is for |
Code blocks
You may be wondering how those text blocks appeared above without the BBCode inside them being formatted. This is one of the features of a code block - everything inside them is treated as plain text, and not formatted. This is good for posting snippets of code. To post a code block using the Markdown style, surround the code with three backtick characters (that's the ` character). This will align the code block to the left to avoid unnecessary whitespace.```
Surround your text with three backticks like this to format it as code.
```
[pre]. It stands for "preformatted". Unlike backtick blocks, preformatted blocks will retain all whitespace, including at the start of lines.
[pre]All the text inside this tag will be a code block. All whitespace inside this block will be retained.[/pre]Syntax highlighting
function javascript() { console.log('hello!'); }js as the example language):
[pre=js]function javascript() { console.log('hello!'); }[/pre]```js
function javascript() { console.log('hello!'); }
```
- PHP -
php - Windows batch -
dos,bat,cmd - CSS -
css - C++ -
cpp,c,c++ - C# -
cs - INI config -
ini - JSON -
json - HTML/XML -
xml,html - AngelScript -
angelscript - JavaScript -
javascript,js - Force no highlighting -
plaintext
Columns
For complex stuff you might want to present some content in columns, side by side. You can do that by using the columns directive. It looks like this:%%columns=6:3:3
Column 1
%%
Column 2
%%
Column 3
%%- The column widths are specified in the first line, in this case,
6:3:3. These numbers are in respect to the page being 12 units wide. The column widths must add up to a total of 12 or the columns will not work. - You need to specify the same number of content sections as columns in the first line, or the columns will not work.
- On small resolution screens (phones, tablets), the columns will show underneath each other instead of side by side.
Phew! That's everything! I know there's a lot of stuff here, but don't worry too much about it. If you need to do a particular thing, just come back to this page later so you can refresh your memory.
- Categories
- Meta
